Whey Protein: What is Good for You?
Bea
August 21, 2023

Only some supplements have gained as much popularity and recognition as whey protein in nutrition and fitness. It is renowned for its exceptional health benefits and has become a staple for most people to achieve their fitness goals.
However, if you are a gym-goer or a fitness enthusiast, you must be wondering how much truth there is to the immense benefits of whey protein. This article will explore the different types of whey proteins and whether they suit you. Let’s begin.
Protein Functions in the Body
Proteins play a crucial role in various functions within our bodies. Some of the critical parts of proteins include:
- Tissue building and repair – Proteins are the building blocks for tissue growth, maintenance, and repair.
- Hormone production and regulation – Many hormones are proteins or derived from proteins, playing crucial roles in regulating bodily functions such as blood glucose, controlling endocrine glands, etc.
- Immune system function – Proteins are involved in antibody production and immune cell functioning, helping defend against infections and diseases.
- Transport and storage of molecules – Proteins facilitate transporting and storing molecules such as oxygen, lipids, and nutrients.

What Is WPC?
WPC stands for Whey Protein Concentrate. It is a protein derived from milk, specifically from whey, the liquid portion of milk that separates during cheese production. Whey protein concentrate is obtained by removing non-protein components from whey through various separation techniques such as precipitation, filtration, and drying.
This substance contains a mixture of proteins separated from the main milk protein, casein. The protein content of WPC can vary, typically from 25% to 80%, depending on the specific product.
Additionally, it is commonly used in various food products and protein supplements for muscle gain, weight loss, and overall health improvement.

Different Types of WPC and Their Benefits
WPC 30, 50, 80, and 100 are different types of whey protein with various protein concentration levels. The number indicates the percentage of protein in the product by weight. The higher the attention, the more protein and less lactose and fat the product contains.
The most common concentrations of WPC are:
- WPC 30: contains 30% protein, 50% lactose, and 20% fat.
- WPC 50: contains 50% protein, 35% lactose, and 15% fat.
- WPC 80: contains 80% protein, 5% lactose, and 15% fat.
- WPC 100: contains 100% protein, no lactose, and no fat.
Benefits of Whey Protein
WPC 30: This is the least concentrated form of WPC. This type can add protein and calcium to your diet without increasing the calorie intake too much. WPC 30 is appropriate for seniors, children, and vegetarians.
WPC 50: This medium concentrate can increase protein intake and improve muscle growth and maintenance, such as for athletes, bodybuilders, or fitness enthusiasts. It is soluble in a variety of pH conditions.
WPC 80: This is a highly concentrated form of WPC. It can maximize your protein intake and optimize muscle protein synthesis and recovery. WPC 80 is best suited for powerlifters, sprinters, or martial artists. It can also boost the immune system and reduce oxidative stress by increasing glutathione levels for people with chronic diseases.
WPC 100: This type can minimize your lactose, fat, and carbohydrate intake while getting the highest amount of protein and amino acids. It can also help with weight loss by increasing satiety and metabolism. This is best for those who follow low-carb diets or deal with obesity.
What Is the Right Amount of Protein for Your Body?
The amount of protein your body needs depends on various factors, such as age, weight, activity level, and health objectives.
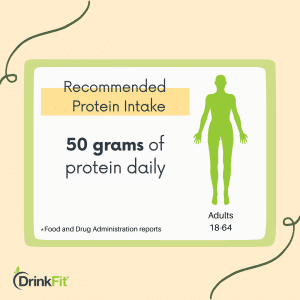
According to reports from the FDA, an average adult in the US must consume about 50 grams of protein daily. However, as this can vary for each individual, you can use an online protein calculator to estimate the optimal protein intake for your body.
Many experts recommend consuming 15–30 grams of protein during each meal for optimal health and muscle growth. If you consume more than this range, it will not necessarily provide any additional benefits.
What Happens When There Is Not Enough Protein?
Protein deficiency can seriously affect your performance if you are a gym goer or a fitness enthusiast. Protein is essential for building and maintaining muscle mass, vital for strength, power, and endurance.
Without enough protein, your body may break down your muscles to get the amino acids it needs, leading to muscle loss, reduced metabolism, and increased risk of injury.
Protein also helps you recover from workouts by repairing muscle damage and reducing soreness. So, lack of it can hinder your recovery, and you may feel more tired and weak.
What Happens When There Is Too Much Protein?
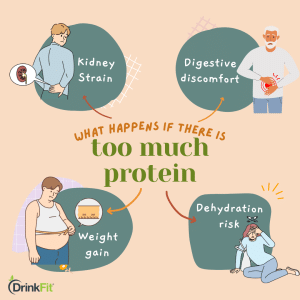
Excessive protein intake can lead to various issues in the body. Here are some potential consequences of consuming too much protein:
- Kidney strain: High protein intake can stress the kidneys, potentially impairing kidney function or exacerbating existing kidney conditions.
- Digestive discomfort: Excessive protein consumption can cause digestive issues such as bloating, constipation, diarrhea, and increased production of gut ammonia, affecting gut health.
- Weight gain: Consuming excessive protein without adequate calorie control can lead to weight gain as excess protein can be converted into fat.
- Dehydration risk: High protein diets may increase water needs, and insufficient hydration can strain the kidneys and lead to dehydration.
Summing Up
Whey protein is a source of high-quality protein. It offers numerous health benefits, including promoting muscle growth and strength, supporting weight loss and appetite control, enhancing immune system function, aiding skin health and wound healing, and nourishing hair and nails. Its richness in amino acids makes it even more valuable.
So, if you have included or are thinking of including whey protein in your diet, this is undoubtedly a good decision. Make sure to choose a product with a concentration suitable for your body.
Leave A Comment
Warning: Undefined variable $post in /home/drinkfit/development.drinkfit.com/wp-content/plugins/code-snippets/php/snippet-ops.php(582) : eval()'d code on line 4
Warning: Attempt to read property "ID" on null in /home/drinkfit/development.drinkfit.com/wp-content/plugins/code-snippets/php/snippet-ops.php(582) : eval()'d code on line 4
Warning: Undefined variable $post in /home/drinkfit/development.drinkfit.com/wp-content/plugins/code-snippets/php/snippet-ops.php(582) : eval()'d code on line 5
Warning: Attempt to read property "ID" on null in /home/drinkfit/development.drinkfit.com/wp-content/plugins/code-snippets/php/snippet-ops.php(582) : eval()'d code on line 5
Warning: Undefined variable $post in /home/drinkfit/development.drinkfit.com/wp-content/plugins/code-snippets/php/snippet-ops.php(582) : eval()'d code on line 28
Warning: Attempt to read property "ID" on null in /home/drinkfit/development.drinkfit.com/wp-content/plugins/code-snippets/php/snippet-ops.php(582) : eval()'d code on line 28

 0
0

